


How Agriculture Technology is Revolutionizing Farming
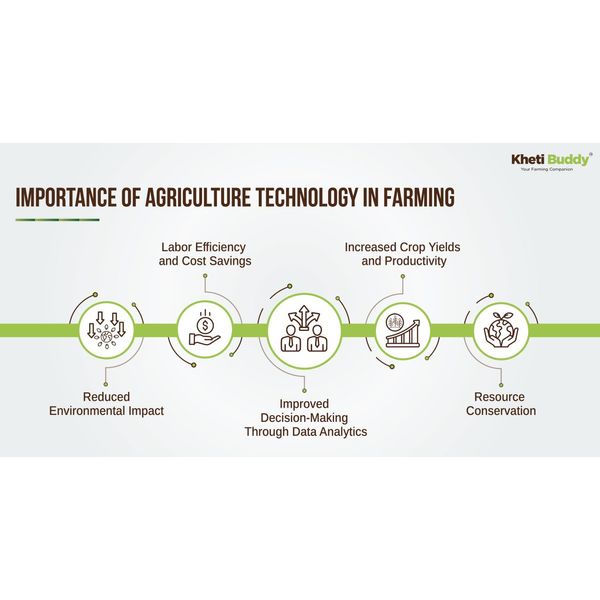
The agricultural sector is at a critical stage. With the global population projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, the demand for food is increasing rampantly. At the same time, there is mounting pressure to adopt sustainable farming practices to protect our planet’s limited resources. This delicate balance between increasing food production and minimizing environmental impact highlights the importance of leveraging advanced agricultural technologies.

The challenge of meeting the increasing demand for food while minimizing the environmental impact is heightened by limited natural resources and the need for sustainable practices. The fine line between fulfilling rising food demands and conserving resources calls for the adoption of innovative technologies. By using advanced agricultural technology, agribusinesses can optimize resource use, boost productivity, and ensure sustainability, thereby addressing both current and future challenges. In this blog, we’ll learn about various agricultural technologies, their use cases, benefits, and how these modern advancements are revolutionizing the farming industry.
It utilizes data and technology to optimize field-level management regarding crop farming.
- GPS-guided equipment: Enables precise planting, fertilizing, and harvesting.
- Soil sensors: Monitor moisture levels, temperature, and nutrient content.
- Variable rate technology (VRT): Allows for the application of inputs such as seeds and fertilizers at varying rates across a field.
Benefits: Precision agriculture boosts productivity by ensuring crops receive the right amount of inputs at the right time. This reduces waste and increases yields. By monitoring soil health and crop conditions, farms can make informed decisions, leading to more efficient use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides. Additionally, precision agriculture reduces environmental impact by minimizing the use of chemicals and conserving water resources, promoting sustainability in farming practices.
This involves the use of genetic engineering to improve crop varieties for better yield, pest resistance, and environmental adaptability.
- Genetically modified organisms (GMOs): Crops engineered for traits such as drought resistance and pest resistance.
- CRISPR technology: Allows precise editing of plant genomes to enhance desirable traits.
- Biopesticides: Biological agents used to control pests without harmful chemicals.
Benefits: Biotechnology increases crop yields by creating varieties that are resistant to pests, diseases, and adverse environmental conditions. This reduces the need for chemical pesticides, lowering production costs and environmental impact. Crops can be engineered to have higher nutritional value, addressing malnutrition in developing regions. Furthermore, biotech crops can grow in previously inhospitable conditions, expanding fertile land and contributing to food security.
It involves using satellites to collect data on crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns.
- Satellite imagery: Provides large-scale data on crop health and soil moisture.
- Spectral analysis: Assesses plant health through light reflectance measurements.
Benefits: Remote sensing technology allows farms to monitor large areas efficiently, identifying problems such as pest infestations or water stress early. This enables timely interventions, reducing crop losses and improving yields. By providing detailed insights into field conditions, remote sensing supports precise irrigation and fertilization, optimizing resource use. Additionally, it aids in long-term planning and risk management by offering data on weather patterns and soil health trends.
It involves using machines and robots to perform repetitive and labor-intensive farming tasks.
- Automated tractors: GPS-guided machines for planting and harvesting.
- Robotic weeders: Robots that identify and remove weeds without damaging crops.
- Harvesting robots: Machines that pick fruits and vegetables with precision.
Benefits: Automation and robotics reduce the labor burden and increases efficiency by performing tasks faster and more accurately than manual labor. Automated systems can operate around the clock, boosting productivity. Additionally, robots minimize human error and reduce the physical strain on laborers, improving safety and working conditions. By optimizing resource use and reducing waste, automation contributes to more sustainable farming practices.
It integrates various farming operations into a single platform for better decision-making and resource management.
- Data analytics: Analyzes data from sensors, equipment, and weather reports.
- Inventory management: Tracks inputs like seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- Financial planning: Manages budgets, expenses, and revenues.
Benefits: FMS streamlines operations by providing a centralized platform for monitoring and managing all aspects of farming. It improves decision-making by offering real-time data and insights to optimize resource use and increase productivity. By tracking inputs and outputs, the software helps in efficient inventory management and cost control. Financial planning tools help in budgeting and forecasting, ensuring financial stability. Additionally, the software improves traceability and compliance with regulations, promoting transparency and accountability.
This technology offers a secure and transparent way to track the supply chain from farm to table.
- Decentralized ledger: Records transactions in a secure, immutable way.
- Smart contracts: Automates and enforces agreements between parties.
- Traceability systems: Tracks the journey of products through the supply chain.
Benefits: Blockchain offers transparency by providing a tamper-proof record of every transaction, from production to sale. This builds consumer trust by ensuring the authenticity and safety of food products. Smart contracts streamline transactions and reduce administrative costs by automating agreements and payments. Traceability systems help in identifying and addressing issues such as contamination or fraud quickly, minimizing risks and ensuring food safety. By promoting transparency and accountability, blockchain supports sustainable and ethical farming practices.
AI and big data analytics transform vast amounts of data into actionable insights for better farming decisions.
- Predictive analytics: Forecasts crop yields and disease outbreaks.
- Machine learning algorithms: Analyzes data to optimize farming practices.
- Decision support systems: Provides recommendations based on data analysis.
Benefits: AI and big data allow predictive analytics, helping anticipate and mitigate risks such as pest infestations and adverse weather conditions. Machine learning (ML) algorithms optimize farming practices by identifying patterns and trends in data, leading to more efficient use of resources. Decision support systems offer personalized recommendations, improving crop management and boosting yields. By making use of data, AI improves precision and accuracy in farming operations, promoting sustainability and reducing costs.
This technology involves growing crops in stacked layers or vertically inclined surfaces, often in controlled environments.
- Hydroponics: Growing plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water.
- Aeroponics: Growing plants in an air or mist environment without soil.
- Controlled environment agriculture (CEA): Using technology to control temperature, humidity, and light.
Benefits: Vertical farming maximizes space usage by growing crops in stacked layers, making it ideal for urban areas with limited land. It allows for year-round production in controlled environments, ensuring consistent yields and quality. Hydroponics and aeroponics reduce water usage significantly compared to traditional farming, promoting sustainability. Vertical farming also minimizes the need for pesticides, as controlled environments reduce pest and disease risks. By bringing food production closer to consumers, it reduces transportation costs and carbon footprint.
With the adoption of these advanced technologies, an enormous amount of data is generated. To exploit the full potential of this data, it is crucial to have a unified platform that structures, processes, and analyzes it effectively. SaaS-based Agtech platforms play a crucial role in this process. They merge data from various sources, ensuring it is organized and accessible. By applying complex algorithms, these platforms generate insights that support informed decision-making. Quick and informed decisions enhance farming practices, optimize resource use, improve transparency, and identify bottlenecks to reduce unnecessary costs. Effective data management is the backbone of modern agriculture, driving efficiency and sustainability.
Agricultural technology is revolutionizing farming by making it more efficient, productive, and sustainable. From precision agriculture and biotechnology to AI and vertical farming, these innovations address the challenges of increasing food demand and environmental sustainability. By exploiting data and advanced technologies, farmers can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and reduce environmental impact.
Discover the future of farming with Khetibuddy’s Unified Agtech Platform. Our platform integrates advanced technologies to provide extensive solutions for modern agriculture. Join us in transforming farming practices for a sustainable and prosperous future.
