

- Home
- Companies
- Beston Group Co., Ltd.
- Articles
- Quality Control Parameters in Egg Tray ...
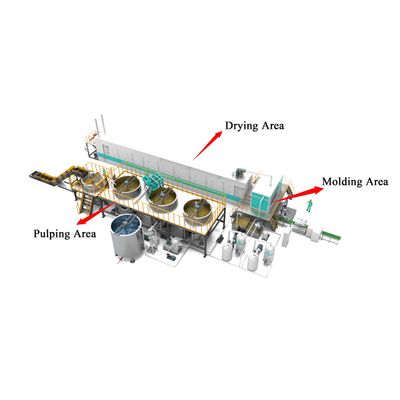
Quality Control Parameters in Egg Tray Molding Machine Manufacturing
The production of an egg tray molding machine demands stringent adherence to quality control parameters to ensure operational reliability, dimensional accuracy, and lifecycle efficiency. Given the mission-critical nature of molded pulp trays in packaging logistics, machine consistency directly influences output integrity and production economics.
Structural Component Inspection
A primary focus in quality control is the inspection of fabricated pulp molding plant components, including the forming mold frame, transfer mold assembly, and drying tunnel structure. Dimensional conformity is verified using coordinate measuring systems to ensure precise alignment of moving parts. Deviations can result in improper mold fitment, misfeeds, and non-uniform tray formation.
Weld joints, particularly in the chassis and mold brackets, undergo non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection. These procedures detect sub-surface inconsistencies that could compromise structural stability under continuous operational stress.
Mold Accuracy and Surface Integrity
The forming mold is the core of any egg tray molding machine. Quality assurance here involves tolerance calibration, cavity symmetry inspection, and vent hole alignment. CNC-machined molds are evaluated for micro-deviations that may affect fiber deposition and water drainage.
Surface roughness plays a critical role in mold release and product finish. Therefore, molds undergo profilometric testing to ensure optimal surface texture. Inconsistent surfaces may cause adhesion, incomplete drying, or torn trays—all of which undermine downstream automation and packing efficiency.
Pneumatic and Hydraulic System Validation
Modern egg tray molding machine integrates pneumatic actuators and hydraulic systems for forming, transferring, and pressing operations. Leak testing, pressure stability checks, and response calibration are part of the quality audit process. Actuation timing must remain synchronized across the production cycle to prevent operational misalignment.
Control valves, solenoids, and air lines are tested for responsiveness and durability under simulated production conditions. Fatigue testing identifies potential failures in prolonged cycles, ensuring machine readiness for high-throughput environments.
Automation and PLC Programming Validation
Programmable logic controller (PLC) systems govern machine logic and operational sequencing. Quality control teams perform dry runs and live-feed simulations to validate timing protocols, interlock sequences, and sensor responses. Any lag in feedback loops or logic errors can result in tray misalignment, jamming, or mechanical damage.
Firmware is tested against industry-specific standards to ensure stability and cybersecurity resilience, particularly for units integrated with remote diagnostics or IoT-based monitoring.
Drying Efficiency and Thermal Distribution
In machines equipped with integrated drying systems, uniform thermal distribution is essential. Infrared thermography and thermal mapping are used to verify consistent heat application across tray surfaces. Uneven drying causes warping and brittleness, compromising tray stackability and structural integrity.
Fuel consumption rates, exhaust temperature limits, and burner efficiency are measured against calibrated benchmarks. These parameters not only affect tray quality but also determine compliance with environmental emissions standards.
Final Assembly and Operational Benchmarking
Before shipment, each egg tray molding machine undergoes a comprehensive performance test, including trial production with standardized pulp slurry. Output consistency, mold cycle speed, water recovery efficiency, and tray ejection rates are documented.
Any deviations trigger root cause analysis and corrective action protocols. Only after passing all performance thresholds is the machine cleared for packaging and dispatch.
Conclusion
The manufacture of an egg tray molding machine requires precise quality control across mechanical, hydraulic, thermal, and software domains. Consistency in these parameters ensures that end users receive machinery capable of producing uniform, high-strength trays at commercial scale. Quality control is not a peripheral function—it is embedded into every stage of machine engineering to uphold industry standards and client expectations.
